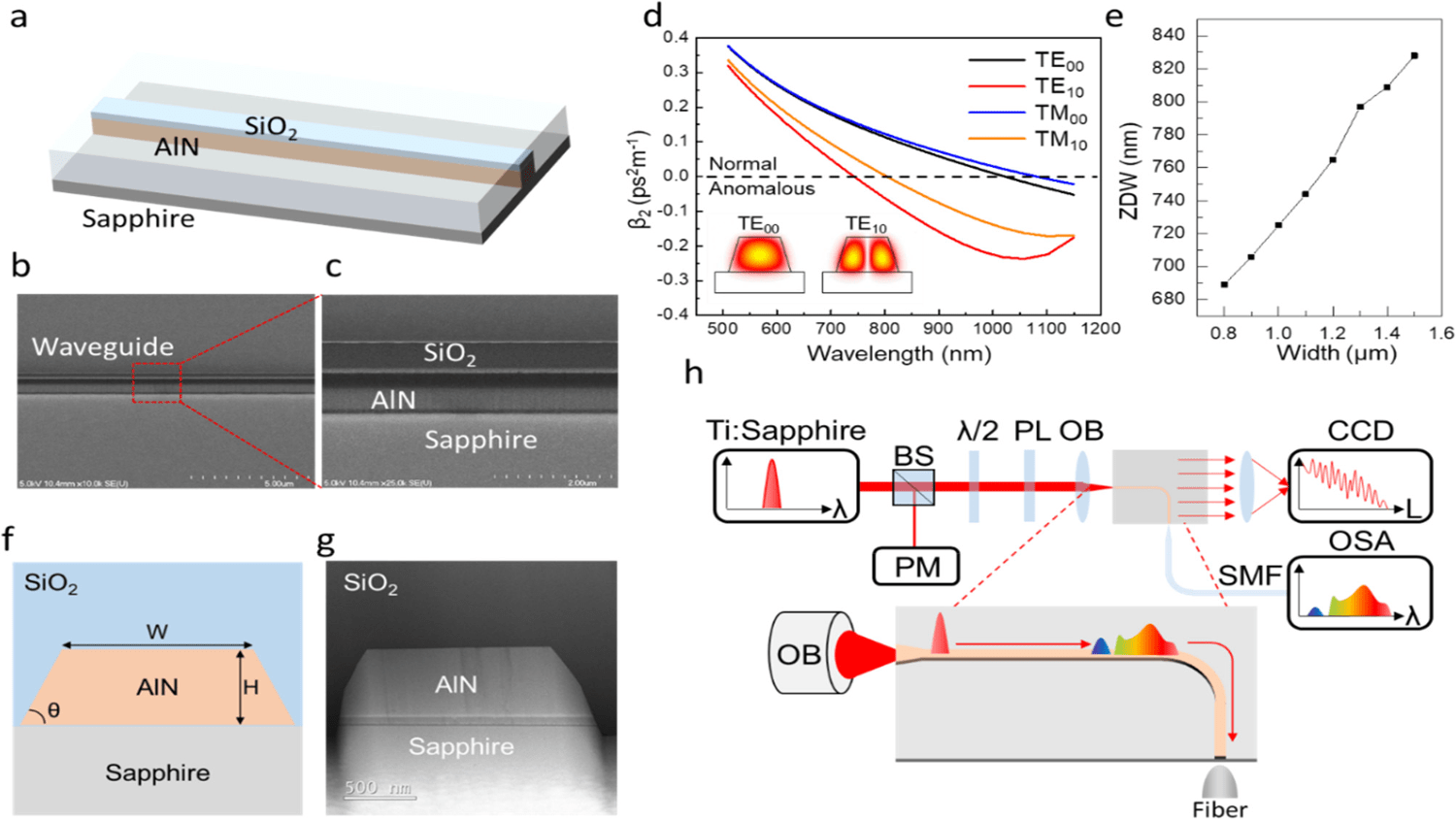
Optical sources emitting in the ultraviolet (UV) to near-infrared wavelength range are an enabling tools for a wide variety of applications. To achieve broadband coherent generation within visible and UV spectrum, one fundamental obstacle is the strong material dispersion which limits efficient frequency conversion. Previous works have addressed this challenge by either using high input energies or delicate resonant structures. In this work, a simple device system is proposed to tackle the problem. Single crystalline aluminum nitride material with a threading dislocation density less than 109 cm–2 was used to provide broadband transparency, and a high order waveguide mode (transverse electric, TE10) was used to create anomalous dispersion near 800 nm, in which soliton fission processes are supported. As a result, supercontinuum generation from 490 nm to over 1100 nm with a second harmonic generated band covering from 407 to 425 nm is achieved with the total on-chip pulse energy of 0.6 nJ.
Chen’s Paper on Supercontinuum Generation Published in ACS Photonics!